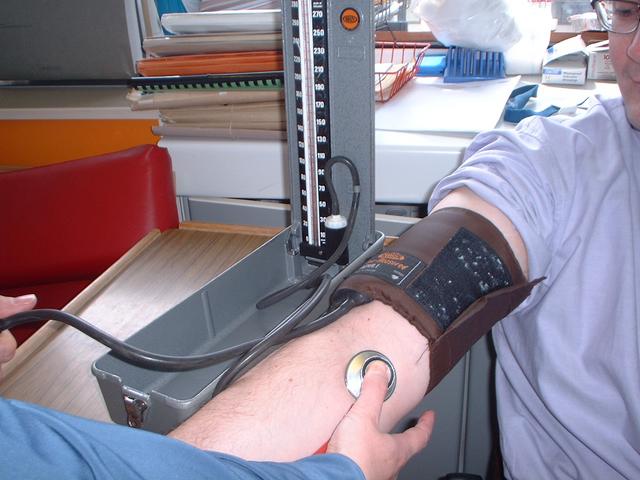
Blood pressure is defined as the force that is pushed along the arteries every time the heart beats. Therefore, blood pressure is a measure of how hard the heart has to work to pump blood.
The pumping action is known as systolic pressure. When the heart is at rest, between beats and the blood pressure falls, is known as diastolic pressure. Blood pressure is measured using a blood pressure cuff and recorded as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. The top number indicates the systolic pressure and the bottom indicates the diastolic pressure. Normal blood pressure is lower than 120/80. Blood pressure in children is much lower than in the adults since pressure rises as a person ages.
The systolic and diastolic reading of 140/90 or higher indicates high blood pressure. This can result in a faster heartbeat as the heart tries to pump the blood. This could lead to stroke, heart attack, and kidney problems.
Severe medical problems can cause blood pressure to rise. Arteries may become hardened and narrowed with cholesterol plaque and calcium, resulting in the heart having to pump harder.
Blood pressure is important to pay attention to as high blood pressure is linked to hypertension, which leads to heart attack.
Ask your doctor about your blood pressure.